本文研究并解释delete [ ]操作符如何确定动态数组的元素个数。
本文转载自重庆大学2019级风流倜傥的于卓浩同学的文章:https://puluter.cn/20200331/delete/
[上述形容词是海洋饼干叔叔加的,与事实相符]
稍有修改。
1. 简介
在面向对象编程中,我们经常会用到这样的动态分配数组:
1 | Person* a = new Person[100]; |
在上述申请数组的过程中,我们使用到了new []这个表达式来完成,它会调用类的构造函数初始化这个数组的所有对象,有多少对象,就会执行多少次构造函数。
如果我们用完了这个数组,想要释放空间,就需要调用:
1 | delete[] a; |
在这个过程中,我们使用了delete[]操作符来完成对象释放。
但是两个问题出现了:
如何知道a数组的内存空间大小?
如何知道要调用几次析构函数(a数组的元素个数)?
显然,想要知道数组有多长,我们必然要存下这个数组的长度。C++中也正是这么做的。本文讨论具体工作原理。
2. 结合代码的分析
注:本文适用于64位mingw。在32位mingw下后文内8字节应为4字节,long long应为int。
我们先定义一个自定义的类。
1 | class Yu { |
同时,在main中声明一个长度为len(20194134)的Yu类型的数组,再获取该数组开头的地址并打印。
1 | const long long len = 20194134; |
输出为:Address for the Array: 0x2670048
理论上,20194134个Yu对象,总共需要 20194134 x sizeof(Yu) = 80776536字节的空间。实际申请的堆(自由内存区)空间稍有出入,我们可以通过重载new [ ]操作符来研究。
我们重载new[]了操作符:
1 | void* operator new[](size_t sz){ |
在这个过程中,我们打印四个关键数值:
- 数组的长度(len)
new[]过程中实际申请的内存空间大小(sz)- 数组理论上需要的内存空间 (数组长度 x sizeof(Yu) = len x 4 )
- 实际空间与理论空间的差 ( sz - len x 4)
上述程序的执行结果为:
1 | |Length: 20194134 |
这里会发现,编译器传递给new [ ]操作符的空间大小比实际需要多8个字节。而8个字节,恰好是一个long long变量的大小,实践中,这8个字节用于存储动态数组的元素个数。
为了弄清楚这8个字节的具体位置,我们重载了delete [ ]函数:
1 | void operator delete[](void *o){ |
1 | int main(){ |
最后几行的输出为:
1 | Address for the Array: 0x2670048 |
成了!我们发现,解构时得到的地址(0x2670040)恰好是数组的地址(0x2670048)减8。
即:0x2670048 = 0x2670040 + 8
接下来,我们更进一步,取出数组地址-8对应地址的一个long long变量,看一下它的值会是什么.
接下来获取该数组前的8字节,识别为long long并打印。
1 | int main(){ |
输出为:
1 | Address for the Array: 0x2670048 |
代码给出的结果证明了前述的猜想:自定义类数组前的8个字节,是一个long long类型的变量,储存了该数组的长度。
3. 结论
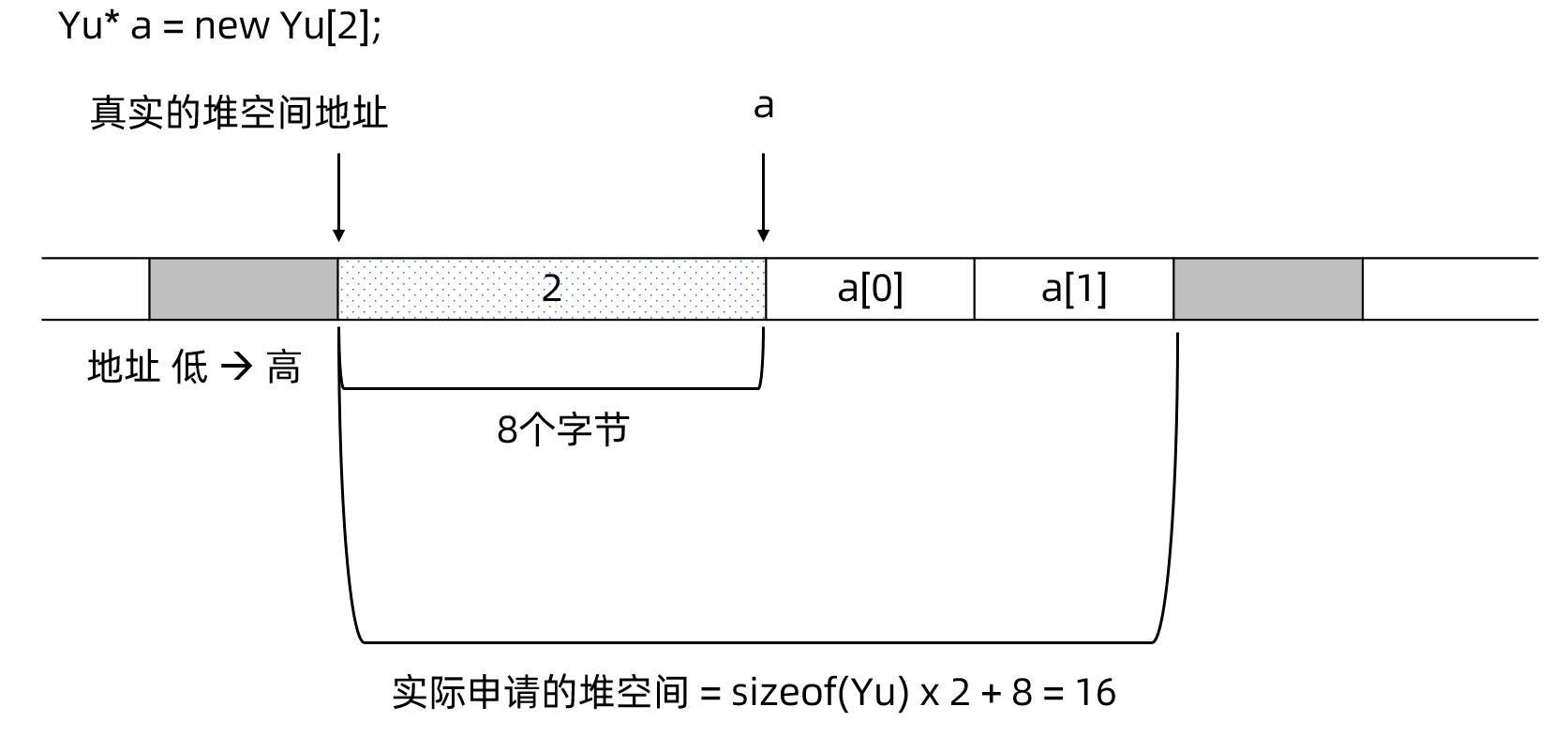
我们以Yu* a = new Yu[2]为例进行说明。表面上,我们需要sizeof(Yu) x 2共8个字节的空间,但事实上,new [ ]操作符会从堆里申请8 + 8 = 16个字节的空间。其中,前8个字节用于存储数组的元素个数,后续空间用于存放数组元素。具体到本例,变量a得到的是数组首元素的地址,它事实上等于真实的堆空间地址 + 8!
当delete [ ]a被执行时:
- delete [ ]操作符会把a值 - 8,获得真实的堆空间首地址;
- 从堆空间首地址获得数组的元素个数(本例为2);
- 依据元素个数及a值逐个执行全部数组元素的析构函数;
- 最后,以堆空间首地址为依据,通过free( )函数向操作系统归还堆空间。
本例中,如果执行delete a而不是delete [ ]a,可能导致两个后果:
- 仅有数组的首元素被正确析构;
- 释放堆空间时向操作系统提供的地址是不正确的,后果未知。
正是基于上述理由,书里反复强调,new/delete, new [ ] /delete [ ]要配对使用。
4. 完整实验代码
1 |
|
完整输出:
1 | Size of long long: 8 |